Introduction to Semiconductors
The Foundation of Modern Electronics


Table of Contents
What Are Semiconductors?
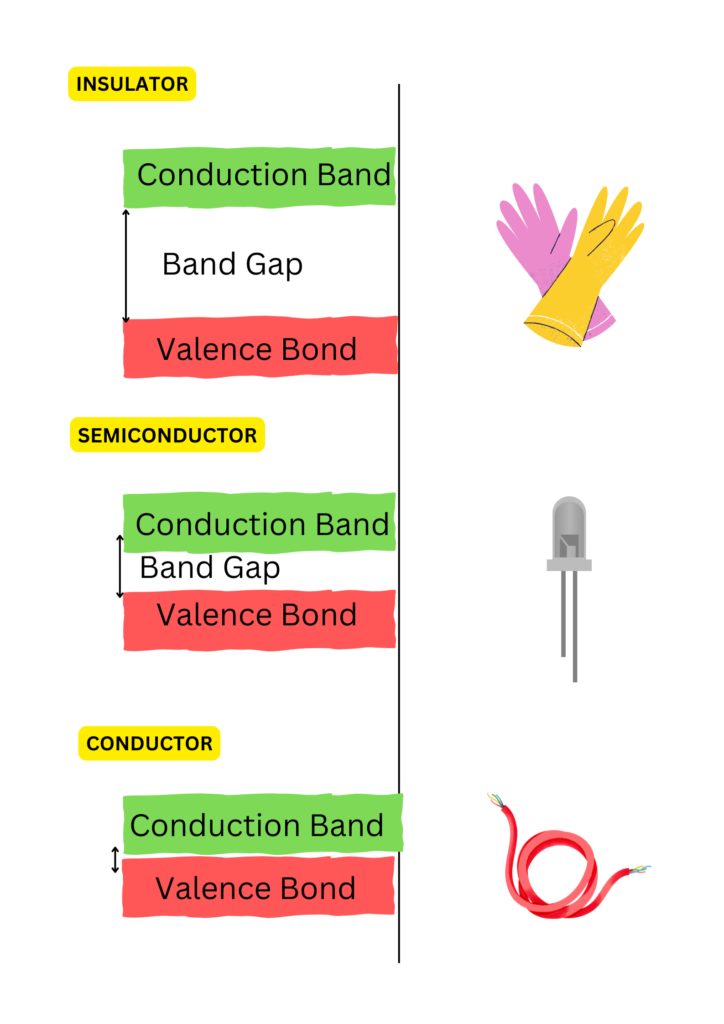
At its core, a semiconductor is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (such as copper) and an insulator (like rubber). This unique property makes semiconductors essential for controlling electrical currents in a wide range of electronic devices.
Connectivity :
- Conductors (e.g., copper) allow electricity to flow freely through them.
- Insulators (e.g., glass) block electrical flow.
- Semiconductors, on the other hand, can be modified to either allow or block electrical current based on external conditions (such as voltage or temperature).
The ability to precisely control electrical current in semiconductors makes them essential for creating switches and amplifiers—key components in everything from computers to solar panels.
Types of Semiconductors
1. Intrinsic Semiconductors:
These are pure semiconductor materials, with no added impurities. They rely purely on the properties of the semiconductor material itself (such as silicon or germanium) to conduct electricity.
- Example: Pure silicon is an intrinsic semiconductor. It has an equal number of electrons (negative charge carriers) and holes (positive charge carriers).
2. Extrinsic Semiconductors:
These are semiconductors that have been intentionally “doped” with impurities to alter their electrical properties. This doping process allows for better control over their conductivity.
- N-type Semiconductor: In this type, an element with extra electrons (like phosphorus) is added, which provides more electrons as charge carriers, giving the material a negative charge.
- P-type Semiconductor: In contrast, an element with fewer electrons (like boron) is added, creating more holes than electrons. These holes act as positive charge carriers.
Materials Used in Semiconductors
The most common materials used in semiconductor manufacturing are silicon, germanium, and various compound semiconductors. Each has unique properties that make it suitable for different applications

Silicon (Si):
Silicon is by far the most widely used material in semiconductors. It’s abundant in nature, relatively cheap, and has excellent thermal and electrical properties. Silicon is the backbone of most modern electronic devices, including computer chips and solar cells.
- Fun Fact:
Silicon Valley, the tech hub of the world, was named after the heavy use of silicon in the semiconductor industry.
2. Germanium (Ge):
Germanium was one of the first materials used in semiconductor devices. It has excellent electrical properties, but it’s less common today due to the cost and thermal sensitivity compared to silicon. However, it still finds use in high-speed electronics and fiber optics.
3. Compound Semiconductors:
These include materials like gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium nitride (GaN). These semiconductors are used in specialized applications such as LEDs, high-frequency devices, and even solar panels. Compound semiconductors can offer faster operation speeds and better performance in specific scenarios compared to silicon.
Why Are Semiconductors Important?
Computing:
The microchips inside computers and smartphones are made of billions of transistors, which are built using semiconductor materials. These transistors can switch electrical signals on and off at lightning speeds, making data processing possible.
Energy:
Solar cells rely on semiconductors like silicon and GaAs to convert sunlight into electricity, powering everything from homes to spacecraft.
Automotive:
Modern cars, especially electric vehicles (EVs), are packed with semiconductor devices that control everything from battery management to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Telecommunications:
Wireless communication, from 4G/5G networks to satellite communications, depends on semiconductor technology for fast and reliable signal processing.
Conclusion
Semiconductors are the unsung heroes of the technological world. These materials might be hidden inside microchips and devices, but their impact is immense. As we move forward into the future of electronics, understanding the fundamentals of semiconductors will help us appreciate the leaps in technology that have become so integral to our lives.
In the next blog, we will dive deeper into semiconductor devices, such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, and explore how they function to control electrical signals in the digital age.


